What Is Blockchain Technology? the History of Blockchain Technology
October 23, 2021


Blockchain technology, which Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many others use, is the hottest thing in technology right now. We could find out about them easily anywhere and at any time. Many people buy them or keep an eye on how much they are worth. So, just what is Blockchain? What’s the point?
In this blog, we’ll talk about the basics of Blockchain for people who aren’t tech-savvy or are just starting out and want to see the big picture of the Blockchain world.

History of Blockchain
Back to history, from 2007 to 2009, there was a world financial crisis that affected everything (economics, politics, social life, etc.) in the world. The fall of Lehman Brothers was seen as the most famous economic failure in the United States. It was called a Unique point of failure.
At the same time, Satoshi Nakamoto wrote a paper called Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. In his/her (we still don’t know who this student is) paper, it was said that Cryptocurrency (the first known example is Bitcoin) could distribute trusts to get rid of Unique of failure. And the technology that makes this system work is called Blockchain.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a Chain of Blocks. Yes, what simple it is!
In advance, Blockchain is:
- A fully decentralized system is one in which there is no central authority in charge of running, monitoring, or changing the network.
- A peer-to-peer distributed ledger: Each node in the Blockchain network has the same job and holds an identical copy of the Blockchain state (blocks, transactions, etc.).
- Cryptographically safe: Blockchain is safe because it uses a bunch of algorithms to control how the system works.
- Content that can’t be changed: Once something has been written to Blockchain, it can’t be changed.
- Only adds new blocks: Blockchain’s consensus mechanism could add new blocks.
- A consensus mechanism is a way for peers in a network to agree on something. If nodes left this out, they could add new blocks to the Blockchain.
Recommended reading: Top Blockchain Companies
What’s Inside Ethereum Blockchain?
Since Ethereum is the most well-known Blockchain so far, we’ll take a closer look at how it works.
1. Nodes
A laptop, computer, or even a phone that is connected to the Internet and works as part of the Blockchain network.
Node’s duties:
- Replicate Ethereum blockchain state
- Forward transactions to the network
- Answer queries
- Verify/ Serve as the witness for new blocks
Recommended reading: Navigating the AVAX to ETH Transition: Strategies and Considerations
2. Blocks
The most basic part of Blockchain is the Block, which includes a block’s hash, a hash from the previous block (if it’s not the first block, also called the Genesis block), a timestamp, a nonce, and a Merkle Root to track back the transaction.

Using Block Explorer tools like Etherscan, we can see Block’s information as below:
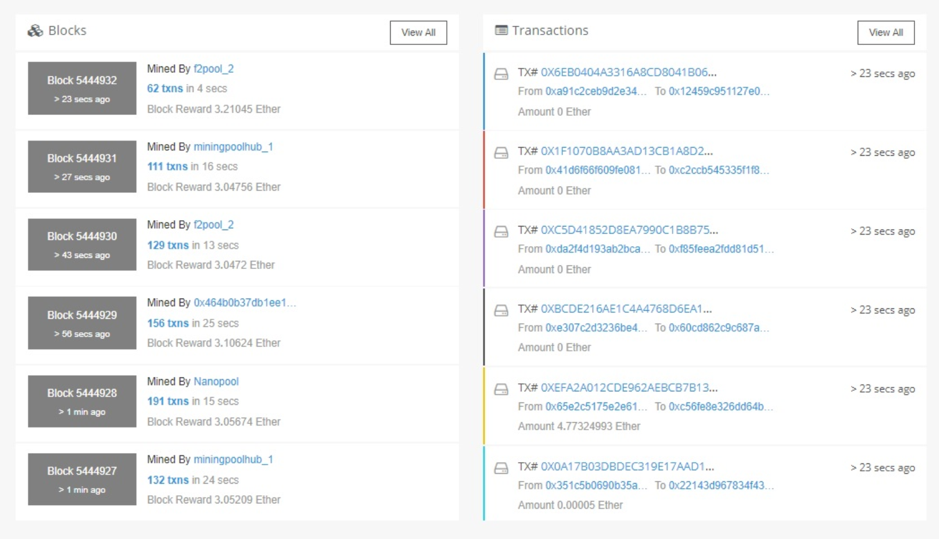
3. Consensus
The leader or a group of people make all decisions. A blockchain can’t do this because it doesn’t have a “leader”. For Blockchain to make decisions, “consensus mechanisms” need to be used to reach a consensus.
Proof-of-Work is the most popular way to reach a consensus (aka POW). In this blog, we will only talk about POW as the main consensus so that it is easier to understand how Blockchain works. But there are a lot of consensus or proof ideas out there. You can learn more here.
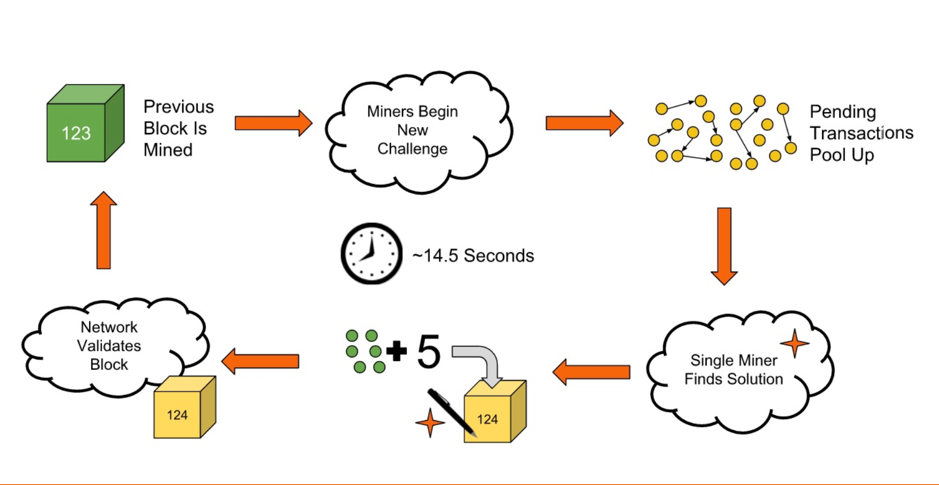
Proof-Of-Work
Satoshi Nakamoto, who made Bitcoin, solved the problem by coming up with the “proof of work” protocol.
This process includes these steps:
- Nodes (miners) add a “nonce” to a block to solve a challenge in order to add a new block. The nonce can be any hexadecimal number at random.
- After that, add a nonce to the block information and hash it. Check the result.
- If the hash conditions are met, they will tell the network that they have found the desired nonce and win this challenge. If not, they will keep changing the nonce’s value at random until they get the result they want. This task is very boring, takes a long time, and requires a lot of processing power.
- If a miner won the challenge, they could get a reward for the time and computing power they used. Then, this miner will add a new block to the Blockchain that is already there.
Mining is the term for all of these steps. It could be summed up by the picture below:
4. Smart Contracts
Nick Szabo came up with the idea in the late 1990s. A smart contract is a computer protocol that is meant to make it easier, more reliable, or more legal to negotiate or carry out a contract.
Smart contracts let transactions happen without the need for a third party. These transactions can be tracked and can’t be changed.
Where to use Smart Contract?
Smart Contract could be helpful in a number of ways, including:
- Government: Imagine that your voting system could run itself without a central, trustworthy authority. Because hackers have access to so many computers, they can no longer change or manipulate the system.
- Supply chain: If I get cash on delivery at this location in a developing or emerging market, then this other product, many, many links up the supply chain, will cause a supplier to make a new item because the existing item just got delivered to that developing market. Paper-based systems, in which forms have to go through a lot of people to get approved, slow down supply chains and make them more vulnerable to loss and fraud. This problem is solved by the blockchain, which gives everyone on the chain a safe, easy-to-use digital copy and automates tasks and payments.
- Real Estate: In real estate, smart contracts can help you make more money. Usually, if you wanted to rent your apartment to someone, you’d have to pay a middleman like Craigslist or a newspaper to get the word out, and then you’d have to pay someone again to make sure the person paid rent and kept their word. The ledger helps you save money. All you have to do is pay with bitcoin and put a code for your agreement on the ledger. Everyone can see, and you automatically get what you want. Brokers, real estate agents, hard money lenders, and anyone else who works in the real estate business can make money from it.
- And even more like Healthcare, Automobile, Management, Exchange Market,…
Taking advantage of Smart Contract in Ethereum, with the language named Solidity, developers could adopt and develop their own Smart Contracts applications (aka DApps), e.g. CryptoKitties, CryptoZombies, …
The Three Types of Blockchain
So far the Blockchain world has 3 types:
1. Public
- Completely opened
- Anyone can read, write, or add new blocks to the chain.
- Public Blockchain is shown by Bitcoin and Ethereum Blockchain.
2. Private
- Invitation-only: Only nodes that are verified and have permission from nodes that run the system or rules that have already been set could join.
- One organization is the only one that can write information and verify transactions.
- Read permission can be open to everyone or limited, depending on the organization that is running it.
- This kind of Blockchain is good for big businesses or organizations that want to run their own Blockchain.
- Representation of Private Blockchain is Hyperledger
3. Permissioned/ Consortium/ Federated
- A hybrid between public and private blockchains.
- Read permission is only available to permissioned parties.
- The consensus process is controlled by a pre-selected set of nodes.
- Representation of Permissioned Blockchain is Hyperledger.
Blockchain Evolution
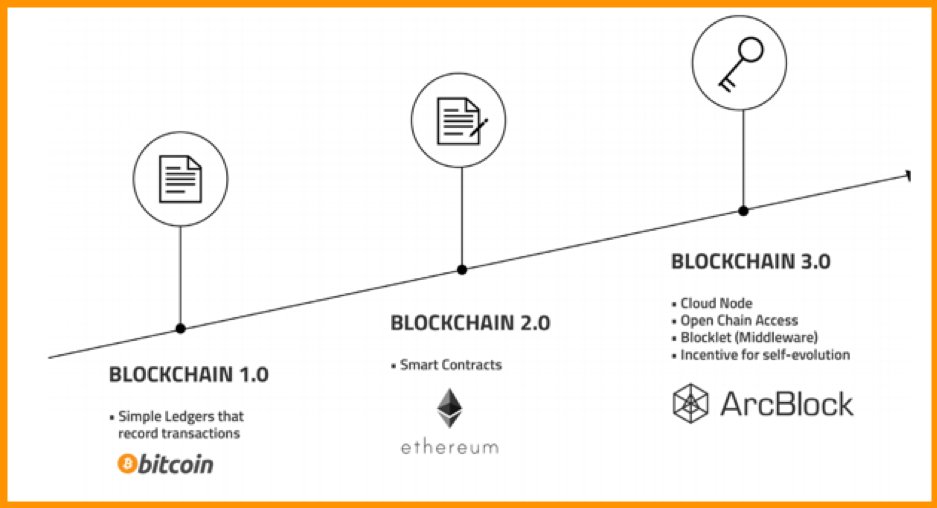
As you can see, Blockchain 1.0 is just a ledger that keeps track of incoming transactions. This was the first use case Satoshi Nakamoto gave for Bitcoin.
We could interact with Blockchain 2.0, which uses Smart Contracts, through Blockchain 2.0. We could also put a logical business layer on top of Smart Contract and end-user applications (aka DApps). Ethereum is the platform that most people use to talk about Blockchain 2.0.
But the technologies that came before Blockchain had their own problems, like scalability,…
Blockchain 3.0 was the first step toward fixing the problems with the previous version of Blockchain. ArcBlock is known as the first place where Blockchain 3.0 was shown off.
Blockchain in Healthcare – It Challenge
With blockchain in healthcare, the paper was chosen from over 70 submissions from a wide range of people, organizations, and companies that talked about how blockchain technology could be used in health and health IT to protect, manage, and exchange electronic health information.
A team from Deloitte Consulting LLP won a Blockchain Ideation Challenge put on by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (ONC).
The 5 Ways to Invest in Blockchain Technology
Investing in Blockchain is one of the hottest trends in the financial markets, and it could change the way traditional business models work in a number of fields.
The good news is that there are many ways to invest in blockchain technology, giving investors the chance to take advantage of what this new technology has to offer.
- Pure Blockchain Technology Play
- Angel Funding and Startups
- Crowdfunding
- Blockchain Penny Stocks
- Stockpiling Bitcoin
The 3 Free Courses to Learn Blockchain Technology
The top three courses for learning about blockchain technology will teach you the basics, such as what blockchain is and how it works. It will also show you how to make your own private network and a smart contract.
- Blockchain — Principles and Practices.
- Ethereum for Beginners: Build a Hello World Blockchain App.
- Blockchain Fundamentals.
Blockchain Advantages – Combining IoT with the power of blockchain
- Generate new efficiencies: IBM Blockchain IoT uses data from IoT devices and sensors to streamline processes and create new business value across your ecosystem.
- Rely on added security: With the Watson IoT Platform, you can choose which data you want to manage, analyze, and customize. This gives you more security.
- Gain greater flexibility: The IBM Blockchain Platform is open, can work with other systems, and was made for a multi-cloud world.
- Build trust in your IoT data: Each transaction is recorded, put into a data block, and added to a secure, immutable data chain that can’t be changed, only added to.
Conclusion
The Future of Blockchain
From Forbes Magazine. Imagine a technology that could:
- Increase the number of Nigerian girls who finish high school by giving their families money when their daughter has a 90 percent attendance rate.
- Allow a musician to choose a charity to receive 50 percent of the royalties from a particular song.
- Coordinate what resources (financial, medical, etc.) have already been given to a refugee by different aid groups that haven’t been able to “compare notes” this way in the past.
- With a “smart” refrigerator, you can help people save electricity and then automatically give the money you saved to charity.
Blockchain technology is making all of these things more and more possible. Blockchain is still in the “early adopter” stage, but it has a lot of potential for programs that help people all over the world.
Depending on your industry, your company may already be keeping an eye on or experimenting with technologies like blockchain and bitcoin. However, if you want to be a part of social impact programs in the 21st century, you’ll need to know about this change.
We at Designveloper are early adopters of Blockchain technology, which is just starting to become popular. We’re optimistic about the future of applications based on Smart Contracts or Blockchain technology in general. We put on some workshops so that our developers could learn more about Blockchain. If you’re interested, you can find a more technical tutorial on how to make your own DApps here. We’re happy to work with any companies or organizations that are part of the Blockchain World’s beautiful party.
Senior Developer






Read more topics




























































